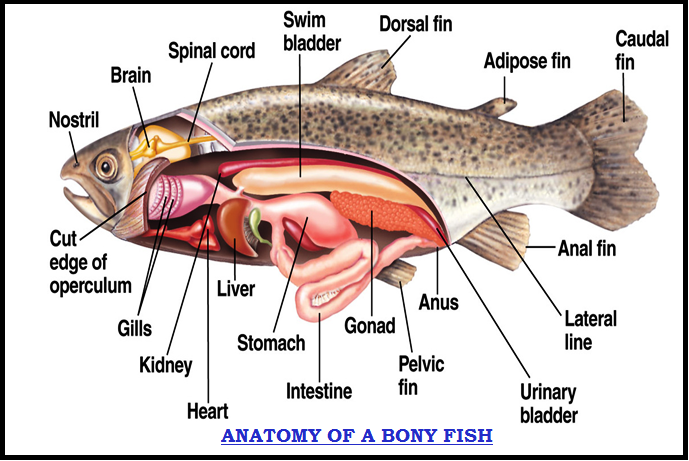
● `color{Brown}"Skeletal system"`:
`star` They have `color{Violet}"cartilaginous endoskeleton"`.
`star` Notochord is `color{Violet}"persistent"` throughout life.
● `color{Brown}"Respiratory system"`:
`star` Gill slits are `color{Violet}"separate"` and without operculum (gill cover).
`star` Due to the absence of air bladder, they have to `color{Violet}"swim constantly"` to avoid sinking.

● `color{Brown}"Circulatory system"` : Heart is `color{Violet}"two-chambered"` (one auricle and one ventricle).
● `color{Brown}"Characteristic organs"` : Some of them have `color{Violet}"electric organs"` (e.g., Torpedo) and some possess `color{Violet}"poison sting"` (e.g., Trygon).

● `color{Brown}"Skeletal system"`:
`star` They have `color{Violet}"cartilaginous endoskeleton"`.
`star` Notochord is `color{Violet}"persistent"` throughout life.
● `color{Brown}"Respiratory system"`:
`star` Gill slits are `color{Violet}"separate"` and without operculum (gill cover).
`star` Due to the absence of air bladder, they have to `color{Violet}"swim constantly"` to avoid sinking.

● `color{Brown}"Circulatory system"` : Heart is `color{Violet}"two-chambered"` (one auricle and one ventricle).
● `color{Brown}"Characteristic organs"` : Some of them have `color{Violet}"electric organs"` (e.g., Torpedo) and some possess `color{Violet}"poison sting"` (e.g., Trygon).